With multiple options for apps and various technologies available, it can get confusing when choosing an app type for your business. Which is absolutely normal as the obvious three (native, web, and hybrid) have their own set of advantages and disadvantages.
So, it is only a matter of understanding all three and answering the question of ‘which app to build?’ in a more learned manner. This is why you are here and I am writing this to make sure you understand all three kinds of apps in the best way possible.
However, before we dive into the details, you need to understand that there is no winner in this situation. It boils down to your own business objectives, app requirements, your budget, and much more.
Now, the majority of the smartphones are running on Android and iOS, so not only you have to decide which technology to pursue in terms of app development but also which platform to build it on; iOS or Android?
The answer to whether to choose Android or iOS depends on certain factors which largely includes the target audience. If your audience uses Apple phones more than Android, then you know which platform to target. However, if you are planning on creating for both and struggling with the budget, then cross-platform app development is your best bet.
Coming towards the apps in question, let’s closely understand what web, hybrid and native apps are all about and which one can best fit our business requirement(s).
Web Apps
A web application, much like a website is accessed through a web browser. You may be wondering, if it is accessed the same way as a website then how does both differ from each other?
Web Apps Vs Websites
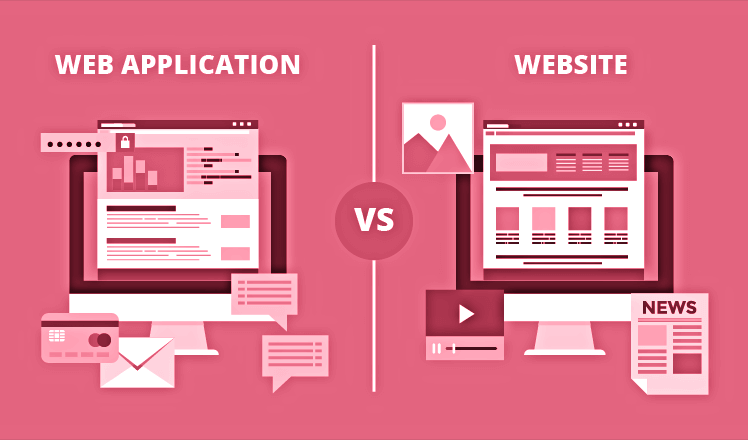
Websites are mostly static and provide information to the users. It is accessible to all visitors. In addition, websites do not require authentication, specifically for sites that are just informational.
Web applications on the other hand are designed to be interacted with by the end-user. The users cannot only read the content but also manipulate it as well. Web apps do require authentication.
A misconception that may arise upon hearing the word ‘app’ with ‘web’ is that they are like regular native apps. This is not the case as web apps do not require to be downloaded and run in browsers. Hence, they do not take up the phone’s memory.
We cannot speak about web apps and not mention Progressive Web Apps.
Progressive Web Apps
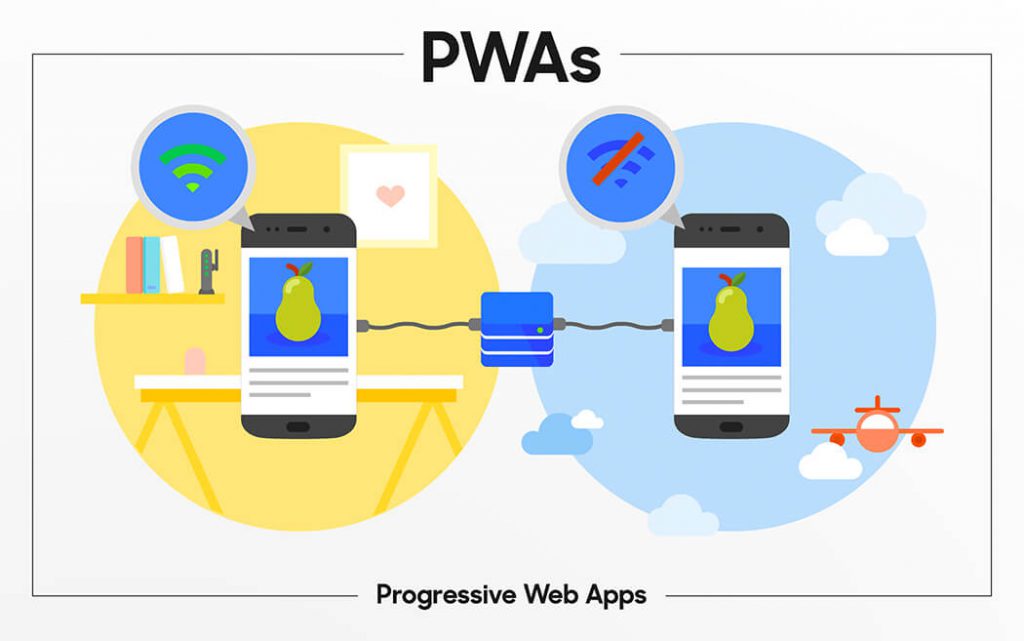
The web has seen significant growth and progress over the years. The web apps that lacked the functionality of an app, are now equipped to behave just like a native app – known as the Progressive Web Apps.
These Progressive Web apps are websites that have app-like features. For instance, they can send push notifications, can be loaded on the home screen, and work offline. Moreover, since they run in the browser, your phone’s battery and storage are spared.
With progressive web apps, you have the advantage to rank in search engines and reach a global audience. However, if a progressive web app doesn’t correlate to your goals or audience, then it is not for you.
Native Apps

A native app is a platform-specific software application built using a specific programming language. For iOS apps, it would be Swift or Objective-C and for Android, it’s usually Java.
Benefits of Native Apps
In order to understand if a native app is the right solution for you, then consider these advantages that will give you a better insight.
Fast and Responsive
Native apps are faster as they reside within the application and make use of the device’s resources. In addition, they are reliable and responsive.
Make Use of Device’s Functionality
As mentioned above, a native app can tap into the device’s resources like a camera, microphone, GPS, compass, so on, and so forth.
Working Offline
Native apps can provide a certain level of functionality without internet connectivity. In other words, if you are commuting and lacking service, you can still open and interact with your app.
For example, take the grocery delivery app. You can open the app, select through items, add them to your cart and when you are back online, you can make the order.
Disadvantages
On the downside, a native app doesn’t come cheap and has longer development timelines. In addition to these drawbacks, they use separate code-base. Meaning, you cannot expect an Android app to miraculously work on Apple phones.
Hybrid Apps
Hybrid apps can be defined as software applications that merge native apps and web apps together. In other words, hybrid apps are web apps that are under the shell of a native app. They differ from progressive web apps and require a download from an app store. Once installed on the phone these hybrid apps run in a webview – which is a browser within your app.
Benefits of Hybrid Apps
One Codebase and Saving Money
Hybrid apps allow you to have one codebase and run your apps on both platforms; iOS and Android. This relieves developers from the hassle of creating two separate apps and saves your investment as well, which in terms of a native app, would be large.
So you are looking at shortened development timelines, less-expensive, and scalable.
Access to Device Features
Like native and progressive web apps, hybrid apps can also make use of the device’s features.
Disadvantages
The downside of Hybrid would be that the performance is not as fast or smooth compared to native apps because of the webview. Moreover, trying to run a Hybrid app on various platforms is not as cheap or simple as one would hope.
Another drawback of the Hybrid app would be the struggle to customize the user experience as close as the platform-specific native apps.
Wrapping Up
By now, you must have a decent knowledge of native, hybrid, and web apps. If you have come closer to deciding on which one to go for, then feel free to connect with AppVerticals, a Professional mobile app development company in Dallas. You will get to meet IT professionals and consultants that will help you decide the best technical and business route for you within the budget. Moreover, you will be provided with after-launch services that will ensure smooth sailing of your product with constant updates and bug fixes.
So, what will it be? Native, Web, or Hybrid app?