Self-driving cars, which were once just a dream, are now becoming a reality. Big car companies and tech companies are working hard to make these cars available to everyone.
The global self-driving car industry is expected to reach $448.6 billion between 2025 and 2035, growing at a 22.2% CAGR.
Self-driving cars have the potential to change transportation in many ways. They could help reduce accidents, traffic jams, and the need for public transportation. However, there are also questions about safety, what is right and wrong, and how to make laws for these cars.
This blog will talk about how AI is making self-driving cars possible. We will discuss the technology behind these cars, the good and bad things about them, and how they will affect other industries.
Whether you love cars and technology or are searching for a software development company for AI integration, this blog is for you.
Let’s discuss it in detail!
What Are Self-Driving Cars?
Self-driving cars are autonomous vehicles (AVs) that can drive themselves! They use special technology to see the road, think like a person, and control the car. This technology helps them steer, stop, go faster, and follow traffic rules.
Levels of Automation
There are six levels of driving automation, ranging from Level 0 (no automation) to Level 5 (full automation):
- Level 0: No automation – the human driver controls everything.
- Level 1: Driver assistance – systems like cruise control or lane-keeping assist help with one aspect of driving.
- Level 2: Partial automation – vehicles can handle steering and acceleration/deceleration, but the driver must remain engaged.
- Level 3: Conditional automation – the car can drive itself in certain conditions, but the driver must take over if needed.
- Level 4: High automation – the car can drive itself in most situations without human intervention, but there are some limitations, such as geographic restrictions.
- Level 5: Full automation – the vehicle is completely autonomous and doesn’t require any human input, no matter the conditions or location.
Currently, most autonomous vehicles on the market are classified as Level 2 or Level 3, with companies like Tesla and Waymo pushing the boundaries of what’s possible. The ultimate goal is to achieve Level 5 automation, where cars will be able to operate without steering wheels or human oversight.
The Technology Behind Autonomous Vehicles
By 2035, approximately 15% of all automobiles will be autonomous.
Self-driving cars use special tools and technology to see, think, and react like a person driving. While people use their eyes and ears to drive, self-driving cars use cameras, computers, and other smart things to understand the road and make decisions.
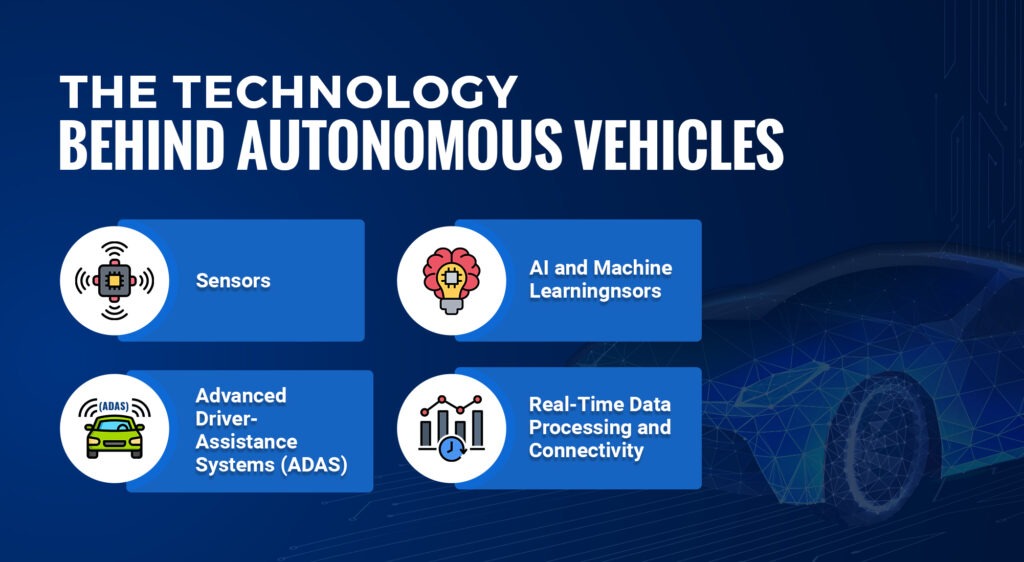
1. Sensors:
Sensors provide the vehicle with data about its immediate surroundings and help it “see” the road:
- Cameras: High-resolution cameras mounted around the vehicle capture images of the road, identifying objects like cars, pedestrians, road signs, traffic lights, and lane markings.
- Radar: It’s particularly useful in low-visibility conditions, such as fog or heavy rain, where cameras may struggle. Radar is typically used for collision avoidance and adaptive cruise control.
- LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging): It works by emitting laser pulses and measuring how long they take to reflect back from surrounding objects. LiDAR can detect obstacles, pedestrians, and road contours with high precision, making it a vital tool for navigation and obstacle avoidance.
- Ultrasonic Sensors: These sensors are typically found around the vehicle’s perimeter and are used for short-range detection, such as during parking or low-speed maneuvers. They help the vehicle identify nearby obstacles when making tight turns or backing up.
2. AI and Machine Learning:
Sensors collect information, but AI and machine learning help computers understand that information and decide what to do. Self-driving cars have smart computers that can learn from different driving situations.
- Data Processing: AI systems analyze this information to detect objects, understand traffic patterns, and make decisions such as when to accelerate, brake, or turn.
- Machine Learning Algorithms: Machine learning helps cars become more efficient and safer as they continue to drive.
- Neural Networks: Neural networks are a type of AI architecture inspired by the human brain. Self-driving cars use neural networks to process visual data, recognize patterns in the environment, and make complex decisions.
3. Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS)
Before achieving full autonomy, many cars today come equipped with advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS). These systems serve as a stepping stone towards fully autonomous driving by offering features like:
- Adaptive Cruise Control: Adjusts the car’s speed to maintain a safe distance from the vehicle in front.
- Lane Keeping Assist: Keeps the vehicle within its lane by making small steering adjustments.
- Automatic Emergency Braking: Detects obstacles and applies the brakes if the driver doesn’t respond in time.
- Blind Spot Detection: Alerts the driver to vehicles in their blind spot when changing lanes.
4. Real-Time Data Processing and Connectivity
For self-driving cars to function seamlessly, they need access to real-time data about road conditions, traffic, and weather. Autonomous vehicles rely on:
- V2X Communication (Vehicle-to-Everything): This technology allows vehicles to communicate with each other, infrastructure (like traffic lights), and even pedestrians.
- Cloud Computing: Self-driving cars are connected to the cloud, where they access high-definition maps, software updates, and traffic data.
Benefits of Self-Driving Cars for the Automotive Industry
Here, we’ll explore some of the most significant benefits that autonomous vehicles offer.

1. Improved Safety
Traditional driving is prone to human error, which accounts for approximately 94% of all traffic accidents. Autonomous vehicles can significantly reduce these risks through:
Self-driving cars are programmed to adhere to traffic laws, maintain safe speeds, and react to hazards instantly, minimizing the risk of accidents caused by distracted or impaired drivers.
With sensors that monitor the environment continuously, autonomous vehicles can detect potential hazards faster than human drivers can. This capability allows for quicker responses, such as sudden braking or swerving to avoid obstacles.
2. Reduced Traffic Congestion
Self-driving cars can communicate with each other to coordinate movements, such as merging lanes smoothly and maintaining optimal distances.
Autonomous vehicles can analyze real-time traffic data to choose the most efficient routes, leading to reduced travel times and less congestion on busy roads.
As self-driving cars can follow each other more closely than human-driven vehicles, roadways can accommodate more cars without increasing the number of lanes, effectively increasing capacity.
3. Environmental Benefits
Autonomous vehicles are designed to optimize acceleration, braking, and cruising speeds, leading to improved fuel efficiency. This optimization can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
The rise of self-driving technology is closely tied to the growth of electric vehicles. Many autonomous vehicles are electric, helping to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and decrease air pollution.
With the potential for shared autonomous vehicle services, there may be less demand for parking spaces in urban areas. This reduction could free up land for parks, housing, or other uses, contributing to better urban planning and sustainability.
4. Enhanced Mobility and Accessibility
Autonomous vehicles can provide vital transportation options for those who may no longer be able to drive, including the elderly and people with disabilities.
This is not enough here! Autonomous vehicles can serve as an effective solution for last-mile connectivity, helping commuters get from public transportation hubs to their final destinations, thus promoting the use of public transport.
5. Economic Growth and Job Creation
The rise of autonomous vehicles will lead to the creation of new industries focused on vehicle technology, infrastructure, and software development, driving job growth in these sectors.
Self-driving trucks can revolutionize the logistics industry by reducing shipping times, cutting costs, and enhancing delivery efficiency. This innovation can lead to lower prices for consumers and increased profitability for businesses.
Challenges Facing Self-Driving Cars
Let’s explore some of the most significant hurdles facing autonomous vehicles today.

Technological Limitations
Autonomous vehicles must navigate diverse and unpredictable driving environments, including busy urban areas, rural roads, and adverse weather conditions. These situations can challenge even the most sophisticated algorithms, as they require an understanding of complex scenarios like pedestrians, cyclists, and sudden obstacles.
While sensors like LiDAR, radar, and cameras are essential for detecting the environment, they are not infallible. Inclement weather, such as heavy rain, snow, or fog, can hinder sensor performance, leading to potential safety risks. Continuous improvements are needed to enhance sensor robustness under various conditions.
Regulatory and Legal Challenges
Many countries and states lack comprehensive legal frameworks governing the use of autonomous vehicles. This absence of regulation creates uncertainty for manufacturers, consumers, and insurers, making it difficult to establish safety standards and operational guidelines.
Before self-driving cars can be deployed on public roads, they must undergo rigorous testing and certification processes to ensure safety. Balancing innovation with safety oversight is critical, as overly stringent regulations could stifle technological progress.
Public Perception and Acceptance
High-profile accidents involving autonomous vehicles have fueled concerns and created a negative perception of the technology. Building public confidence through transparency, education, and proven safety records is essential.
The rise of autonomous vehicles raises concerns about job displacement, particularly for professional drivers in industries like trucking and ridesharing. Addressing these concerns through retraining programs and outlining new job opportunities in the evolving transportation landscape will be crucial.
Ethical Considerations
Self-driving cars will need to make split-second decisions in critical situations, such as avoiding pedestrians or other vehicles. These decisions raise ethical questions about how the vehicle should prioritize lives in unavoidable accidents.
The data collection required for self-driving cars to operate safely raises significant privacy concerns. How this data is used, stored, and shared must be carefully managed to protect individuals’ privacy rights while still ensuring safety.
The Future of Self-Driving Cars in the Automotive Industry
As we look ahead, several trends and developments indicate how self-driving technology will evolve and impact the industry.
Increasing Levels of Automation
Many manufacturers are already introducing Level 2 (partial automation) and Level 3 (conditional automation) features in their vehicles, such as advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS). These systems will continue to improve, leading to greater consumer acceptance and paving the way for higher levels of automation.
Integration with Smart Cities
Self-driving cars will communicate with traffic signals, road signs, and other vehicles, allowing for optimized traffic flow and enhanced safety. This interconnectedness can help reduce congestion and improve overall transportation efficiency.
The data collected from autonomous vehicles can inform urban planners, enabling them to design more efficient road networks, allocate resources better, and improve public transportation systems. This data can also help reduce traffic accidents and enhance pedestrian safety.
Evolution of Transportation Models
Autonomous vehicles will contribute to the growth of Mobility-as-a-Service, where users can access transportation services on demand. This shift can reduce the need for personal vehicle ownership, leading to fewer cars on the road and a decrease in urban congestion.
With self-driving technology, ride-sharing services will become more efficient and affordable. Passengers can enjoy safer and more reliable transportation, making it a viable alternative to personal vehicles.
Collaboration Between Stakeholders
Partnerships between traditional automotive manufacturers and technology firms will be essential for developing advanced self-driving systems. Collaborative efforts can accelerate innovation and lead to more robust solutions.
Regulatory bodies will need to work closely with industry leaders to establish safety standards and legal frameworks that promote innovation while ensuring public safety.
Potential Economic Impacts
While some jobs may be displaced, the rise of autonomous vehicles will create new job opportunities in areas such as technology development, infrastructure maintenance, and data analysis.
Increased efficiency in transportation can lead to significant cost savings for consumers and businesses. Reduced travel times, lower fuel consumption, and minimized accident-related costs will benefit everyone.
Impact of Self-Driving Cars on the Environment
With potential benefits that could lead to a more sustainable transportation ecosystem, it’s essential to examine how autonomous vehicles can contribute to environmental preservation and improvement.

Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Self-driving cars are designed to optimize driving behavior, which can lead to reduced greenhouse gas emissions. By reducing stop-and-go traffic, self-driving cars can contribute to lower carbon footprints.
Many self-driving cars are electric, further reducing greenhouse gas emissions. As the adoption of electric autonomous vehicles increases, the overall carbon emissions from transportation will likely decrease significantly.
As battery technology improves and renewable energy sources become more prevalent, self-driving EVs could be powered by clean energy, further reducing their environmental impact.
Decreased Reliance on Personal Vehicles
The shift toward Mobility-as-a-Service could lead to fewer individuals relying on personal vehicles. This reduction can decrease the total number of vehicles on the road, resulting in less congestion and lower emissions.
Self-driving vehicles can be integrated into ride-sharing and car-sharing programs, promoting shared transportation. Fewer vehicles used by more people can lead to reduced parking needs and lower overall emissions from manufacturing and operating individual cars.
Land Use and Urban Planning
With fewer people owning cars, cities can repurpose parking lots and garages for parks, residential buildings, or commercial spaces. This change can enhance urban livability and reduce urban sprawl.
As self-driving cars become part of smart city infrastructure, urban planners can design road networks that prioritize pedestrian and cyclist safety. This focus can promote alternative modes of transportation and decrease reliance on cars altogether.
Challenges in Environmental Impact Assessment
A comprehensive evaluation of the environmental impact of self-driving vehicles must consider the entire life cycle, including production, operation, and disposal. This analysis will help identify areas for improvement and ensure sustainable practices in the manufacturing of autonomous vehicles.
The rise of self-driving cars may affect public transportation systems. If individuals prefer using autonomous vehicles over buses or trains, there may be a decline in public transit usage, potentially leading to increased emissions.
Wrapping it Up!
The rise of self-driving cars represents a significant leap forward in transportation technology. As we embrace this change, we must remain vigilant, ethical, and forward-thinking to ensure that the transition to autonomous vehicles benefits society as a whole. The journey may be challenging, but the destination promises a new era of mobility that is safer, more efficient, and environmentally friendly.