In 2024, the importance of healthcare data integration, particularly in Mobile App Development Dallas, has never been more pronounced. As healthcare systems worldwide grapple with the complexities of managing vast amounts of patient data, the need for seamless integration across disparate systems has become paramount. Healthcare data integration facilitates the aggregation, exchange, and analysis of data from various sources, enabling healthcare providers to deliver more efficient, personalized, and informed care.
The landscape of healthcare data is constantly evolving, presenting both opportunities and challenges. With the proliferation of electronic health records (EHRs), medical devices, wearables, and other digital health technologies, the volume and variety of healthcare data have reached unprecedented levels. However, this abundance of data also brings challenges, including interoperability issues, data silos, security concerns, and regulatory compliance requirements.
This guide aims to provide healthcare professionals with a comprehensive overview of healthcare data integration best practices in 2024. From understanding the fundamentals of integration to exploring emerging trends and technologies, this guide will offer valuable insights and practical guidance for navigating the complexities of data integration in the modern healthcare landscape.
What is Healthcare Data Integration?
Healthcare data integration involves the process of bringing together data from various sources within the healthcare ecosystem, such as electronic health records (EHRs), laboratory systems, medical imaging devices, wearable sensors, and administrative databases. This integration aims to create a unified view of patient information that is accessible and usable across different healthcare settings and applications. By seamlessly connecting disparate data sources, healthcare data integration enables healthcare providers to access comprehensive patient records, make more informed clinical decisions, improve care coordination, and enhance patient outcomes.
In 2022, healthcare spending in the U.S. rose by 4.1% to $4.4 trillion, averaging $13,493 per capita. This growth mirrors pre-pandemic rates, akin to the 4.1% increase observed in 2019. While government spending surged during the pandemic to tackle healthcare challenges, expenditures notably decreased in 2021. However, utilization of medical goods and services rebounded. By 2022, overall trends in health spending closely resembled those of the pre-pandemic era.
In January 2023, Health Gorilla, an interoperability software platform, unveiled their extensive report titled “The 2023 State of Interoperability.” The findings highlight the growing significance of data exchange in healthcare. Drawing insights from over 130 executive decision-makers in the industry, the report reveals persistent challenges in data quality and sharing.
Key statistics from the report underscore the urgency for robust integration and interoperability:
- 60% of health systems receive duplicate, incomplete, or irrelevant data.
- 69% of health organizations encounter incomplete data.
- 69% of digital health executives face challenges with incomplete data.
- 32% of diagnostic labs don’t contribute to health information exchanges (HIEs), and 76% of those that do, participate only regionally.
- 40% of surveyed EHR vendors acknowledge the potential need to join a Qualified Health Information Network (QHIN) but haven’t prioritized it.
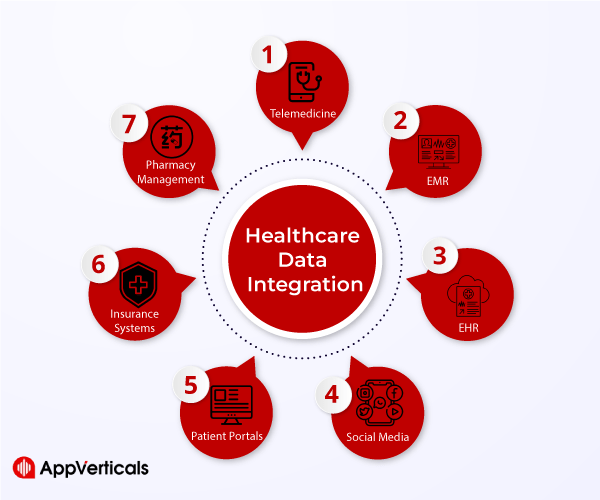
Types Of Healthcare Data And Their Sources
Healthcare data encompasses a wide range of information generated throughout the patient care journey. This includes:
| Type of Healthcare Data | Description | Sources |
| Clinical Data | Patient demographics, medical history, diagnoses, treatments, medications, and laboratory results | EHRs, clinical systems |
| Administrative Data | Billing and insurance information, appointment schedules, ADT data | Healthcare organizations’ administrative systems |
| Patient-Generated Data | Vital signs, activity levels, self-reported symptoms | Wearable devices, mobile apps, patient portals, remote monitoring solutions |
| Research Data | Data from clinical trials, population health studies | Research databases, repositories |
| Public Health Data | Epidemiological data, disease surveillance data, health outcomes data | Public health agencies, organizations |
CReady to revolutionize healthcare?
Hire our expert healthcare app developers today and transform your vision into reality.
Yes Let’s goImportance Of Integration In Enhancing Healthcare Delivery
Effective healthcare data integration plays a crucial role in improving healthcare delivery by:
- Facilitating comprehensive patient care: Integration enables healthcare providers to access complete and up-to-date patient information, allowing for more accurate diagnoses, personalized treatment plans, and coordinated care across multiple providers and care settings.
- Enhancing care coordination and transitions: Integrated data systems enable seamless communication and information sharing among healthcare providers, supporting smoother care transitions, referrals, and handoffs between different healthcare settings.
- Improving operational efficiency: Integration streamlines administrative processes, reduces redundant data entry, and automates tasks such as appointment scheduling, billing, and claims processing, allowing healthcare organizations to operate more efficiently and cost-effectively.
- Supporting data-driven decision-making: Integrated data analytics tools enable healthcare organizations to analyze large volumes of data, identify trends and patterns, monitor population health, and track outcomes, empowering clinicians and administrators to make data-driven decisions that improve patient care and optimize resource allocation.
- Enhancing patient engagement and empowerment: Integration of patient-generated data allows patients to actively participate in their care, monitor their health status, and communicate with their healthcare providers, leading to greater engagement, adherence to treatment plans, and improved health outcomes.
Healthcare Data Integration Use Cases
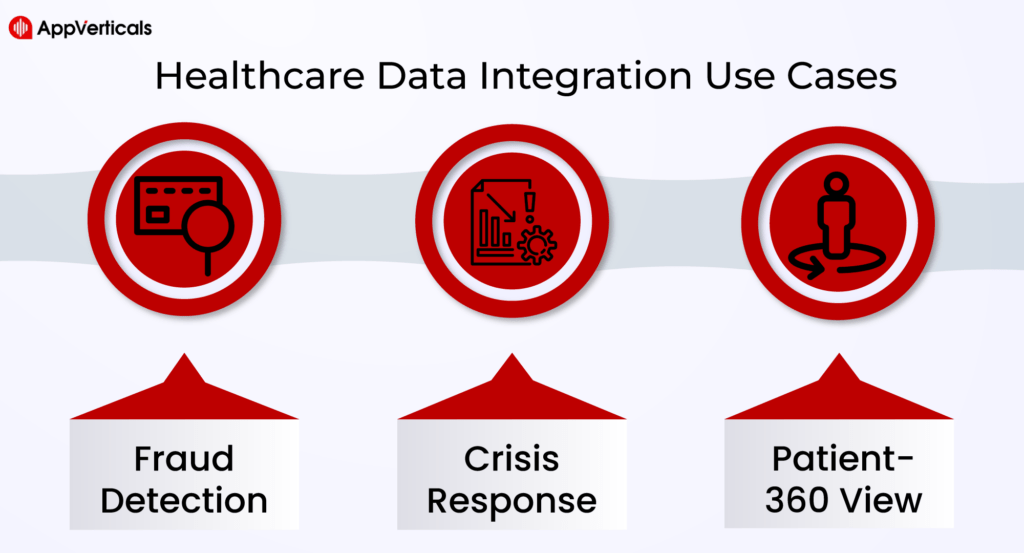
Fraud Detection
Healthcare data integration plays a crucial role in fraud detection by aggregating and analyzing data from various sources, such as claims, billing records, and patient histories. By identifying patterns, anomalies, and inconsistencies in integrated data sets, healthcare organizations can detect fraudulent activities, including billing fraud, identity theft, and prescription drug abuse, and take proactive measures to mitigate risks and protect against financial losses.
Crisis Response
During crises such as natural disasters, pandemics, or public health emergencies, healthcare data integration enables timely access to critical information, including patient records, resource availability, and epidemiological data. Integrated data sets facilitate coordinated response efforts, resource allocation, and decision-making among healthcare providers, public health agencies, and emergency responders, helping to mitigate the impact of crises and save lives.
Patient-360 View
Healthcare data integration enables the creation of a comprehensive “Patient-360” view by aggregating and consolidating patient information from multiple sources, including EHRs, diagnostic tests, medication histories, and social determinants of health. This unified view provides healthcare providers with a holistic understanding of patients’ medical histories, preferences, and risk factors, empowering them to deliver personalized, proactive, and patient-centered care that improves outcomes and enhances patient satisfaction.
Trends in Healthcare Data Integration
1- Adoption Of Cloud-Based Solutions In Healthcare Data Integration
With the increasing volume and complexity of healthcare data, many organizations are turning to cloud-based solutions for data integration. Cloud platforms offer scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, allowing healthcare providers to store, process, and analyze large volumes of data securely. Cloud-based integration solutions also facilitate collaboration and interoperability among healthcare stakeholders, enabling seamless data exchange and integration across different systems and applications.
2- Interoperability Standards And Their Impact On Integration Efforts
Interoperability standards, such as HL7 (Health Level Seven International) and FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources), play a crucial role in healthcare data integration efforts. These standards define common data formats, protocols, and semantics for exchanging healthcare information, ensuring compatibility and consistency across different systems and applications. By adhering to interoperability standards, healthcare organizations can simplify integration efforts, improve data quality and consistency, and facilitate seamless communication and interoperability between disparate systems and stakeholders.
3- Leveraging Artificial Intelligence And Machine Learning For Data Integration
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies are increasingly being used to enhance healthcare data integration processes. These technologies can automate data mapping, normalization, and transformation tasks, identify patterns and correlations in large datasets, and improve data quality and accuracy. AI and ML algorithms can also help healthcare organizations uncover insights from integrated data, predict patient outcomes, and personalize care delivery. By leveraging AI and ML for data integration, healthcare providers can streamline integration processes, reduce manual effort, and unlock the full potential of their data assets.
4- Role Of Blockchain Technology In Securing Healthcare Data Exchange
Blockchain technology holds promise for securing healthcare data exchange and improving data integrity, privacy, and security. By decentralizing data storage and using cryptographic techniques to ensure data immutability and transparency, blockchain can help prevent data tampering, unauthorized access, and data breaches. In healthcare, blockchain can be used to create secure, tamper-proof audit trails for healthcare transactions, authenticate users, and enable secure sharing of sensitive health information between patients, providers, and other stakeholders. While still in its early stages, blockchain has the potential to revolutionize healthcare data integration and improve trust and transparency in healthcare data exchange processes.
Also Recommended: 10 Benefits Of Having A Healthcare Mobile App
Best Practices in Healthcare Data Integration
Healthcare data integration is a complex endeavor that requires careful planning, implementation, and management to ensure success. By following best practices, healthcare organizations can streamline integration efforts, improve data quality, and enhance the value of their integrated data assets. Here are some key best practices in healthcare data integration:
A. Establishing clear data governance policies and procedures
- Data ownership and accountability: Define roles and responsibilities for managing healthcare data, including data stewards, owners, and custodians.
- Data quality management: Implement processes for assessing, monitoring, and improving the quality of integrated data to ensure accuracy, completeness, and consistency.
- Compliance with regulatory requirements: Develop policies and procedures to ensure compliance with healthcare regulations such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) and GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) to protect patient privacy and confidentiality.
B. Choosing the right integration tools and platforms
- Evaluating integration solutions: Assess the capabilities, scalability, interoperability, and security features of integration tools and platforms, such as EHR (Electronic Health Record) systems, HL7 (Health Level Seven International) interfaces, FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) APIs, and middleware solutions.
- Scalability and flexibility considerations: Select integration solutions that can scale to accommodate growing data volumes and evolving business needs while remaining flexible enough to adapt to changing requirements and technologies.
- Integration with existing systems and workflows: Ensure seamless integration with existing healthcare IT systems, workflows, and clinical processes to minimize disruption and maximize efficiency.
C. Prioritizing security and privacy
- Encryption and data masking techniques: Implement encryption, data masking, and tokenization techniques to protect sensitive healthcare data from unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Access controls and authentication mechanisms: Enforce strict access controls and authentication mechanisms to ensure that only authorized users have access to sensitive healthcare information.
- Monitoring and auditing for compliance: Implement monitoring, logging, and auditing mechanisms to track access to healthcare data, detect suspicious activities, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
D. Implementing effective data mapping and normalization strategies
- Standardizing data formats and terminologies: Establish common data formats, standards, and terminologies to facilitate data interoperability and consistency across disparate systems and sources.
- Resolving data inconsistencies and redundancies: Identify and address data inconsistencies, duplicates, and redundancies through data cleansing, normalization, and deduplication processes.
- Ensuring data accuracy and consistency across systems: Implement data validation, verification, and reconciliation processes to ensure the accuracy, consistency, and integrity of integrated healthcare data.
E. Embracing interoperability standards
- FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources): Adopt FHIR as a standard for healthcare data exchange to enable seamless interoperability and integration between different healthcare IT systems and applications.
- HL7 (Health Level Seven International): Implement HL7 standards for messaging and data exchange to facilitate interoperability between healthcare systems, devices, and applications.
- DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine): Use DICOM standards for exchanging medical imaging data and integrating imaging systems with other healthcare IT systems.
F. Promoting collaboration and communication
- Engaging stakeholders across healthcare organizations: Involve key stakeholders, including clinicians, IT staff, administrators, and patients, in the healthcare data integration process to ensure alignment with organizational goals and requirements.
- Establishing cross-functional integration teams: Form cross-functional teams with representatives from different departments and disciplines to facilitate collaboration, communication, and knowledge sharing throughout the integration lifecycle.
- Continuous training and education on integration best practices: Provide training and education programs to empower healthcare professionals with the knowledge and skills needed to effectively participate in healthcare data integration initiatives and leverage integrated data for improved patient care and outcomes.
Crafting Your Ideal Mobile App/Experience Starts Here!
Our skilled team of developers is ready to bring your vision to life. Contact us now to get started!
Yes Let’s goHealthcare Data Integration Challenges
Healthcare data integration faces several challenges, stemming from the complexity of healthcare systems, data sources, regulations, and technology. Some of the key challenges include:
Interoperability
Healthcare IT systems often use proprietary formats, standards, and protocols, making it challenging to exchange and integrate data across different systems and vendors. Lack of interoperability hinders seamless communication and information sharing among healthcare providers, leading to fragmented care delivery and compromised patient safety.
Data Quality and Consistency
Healthcare data is prone to errors, inconsistencies, and duplications due to factors such as manual data entry, disparate data sources, and varying data quality standards. Poor data quality compromises the accuracy, completeness, and reliability of integrated data, undermining its usefulness for clinical decision-making and patient care.
Data Security and Privacy
Healthcare data integration raises concerns about data security and privacy, particularly when integrating sensitive patient health information from multiple sources. Healthcare organizations must implement robust security measures, access controls, and encryption techniques to protect integrated data from unauthorized access, breaches, and misuse.
Regulatory Compliance
Healthcare data integration initiatives must comply with regulatory requirements such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act), GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), and other data protection laws and regulations. Compliance with regulatory requirements adds complexity and costs to integration projects and requires healthcare organizations to implement appropriate safeguards for protecting patient privacy and confidentiality.
Data Governance and Management
Effective data governance is essential for ensuring the integrity, quality, and usability of integrated healthcare data. Healthcare organizations must establish clear policies, procedures, and standards for data governance, including data stewardship, data ownership, data quality management, and metadata management, to govern the lifecycle of integrated data effectively.
Technology Complexity
Healthcare data integration involves integrating data from diverse sources, formats, and platforms, including EHRs, laboratory systems, imaging systems, and administrative databases. Managing the complexity of integration technologies, interfaces, and middleware solutions requires specialized expertise and resources, posing challenges for healthcare organizations with limited IT capabilities and budgets.
Cultural and Organizational Challenges
Healthcare data integration requires collaboration and cooperation among stakeholders, including clinicians, IT staff, administrators, and patients. Overcoming cultural and organizational barriers, resistance to change, and siloed thinking is critical for successful integration initiatives and requires effective leadership, communication, and change management strategies.
Seamless Healthcare Data Integration with AppVerticals Solutions
AppVerticals, as a leading healthcare app development company, offers expertise in healthcare data integration to streamline processes and enhance patient care. Through custom-built solutions and cutting-edge technologies, AppVerticals facilitates seamless integration of disparate healthcare data sources, including EHRs, medical devices, wearables, and administrative systems.
With AppVerticals’ healthcare data integration solutions, healthcare organizations can achieve a unified view of patient information, improve care coordination, and leverage data-driven insights for informed decision-making. Whether it’s optimizing clinical workflows, enhancing population health management, or supporting value-based care initiatives, AppVerticals empowers healthcare providers to harness the full potential of integrated data for better patient outcomes.
Conclusion
Healthcare data integration stands as a critical pillar in modern healthcare delivery, and AppVerticals, with its expertise in on-demand app development, emerges as a reliable partner in navigating this complex landscape. By seamlessly integrating disparate healthcare data sources, AppVerticals empowers healthcare organizations to unlock actionable insights, improve care coordination, and enhance patient outcomes.
Through robust data governance practices, encryption techniques, and compliance measures, AppVerticals ensures the security and integrity of integrated healthcare data, paving the way for informed decision-making and personalized care delivery. With a multidisciplinary approach and innovative solutions, AppVerticals enables healthcare providers to harness the full potential of integrated data, driving efficiency, innovation, and value across the healthcare ecosystem. In an era defined by data-driven insights and patient-centric care, partnering with AppVerticals for healthcare data integration promises transformative outcomes and a brighter future for healthcare delivery.